Unit 3 Biology
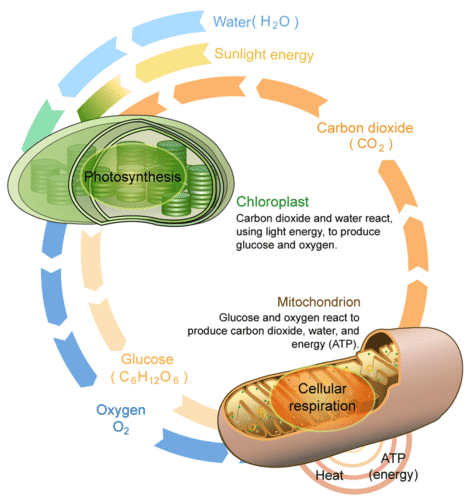
Photosynthesis
Hank Photosynthesis
HANK Osmosis Diffusion
Cell Membrane Ted Talk Tuesday
Amoeba Sisters Cell Membrane
Osmosis
Helpful Osmosis/Diffusion Study Guide with Google Slides
Murder and a Meal Helpful Links
Need more information? Visit these sites for ideas …
Food Chemistry
http://www.sciencecompany.com/sci-exper/food_chemistry.htm
Testing for Lipids, Proteins, & Carbohydrates
http://seplessons.ucsf.edu/node/362
Food Chemistry Testing
http://www.scribd.com/doc/3371524/Food-Chemistry-Testing-SUGAR-STARCH-ETC
Einstein Project – Food Chemistry
http://www.einsteinproject.org/einstein/for+educators/unit+offerings/food+chemistry/default.asp
TEd Ed
How do carbohydrates impact your health? - Richard J. Wood
Chapter 1: Lesson 3 (Cell Book)
Chemical Compounds in Cells
Key Questions
*What are elements & compounds?
*What are elements & compounds?
*What compounds do cells need?
Macromolecules Video
Goals
- Evaluate the application of scientific reasoning, inventions, tools, and new technologies in the study of biology.
- Apply the scientific concepts of hypothesis, inference, law, theory, principle, fact, and observation.
- Analyze structural and functional similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotes.
- Evaluate relationships between structures and functions at various levels of biological organization.
- Analyze the unique properties of water and explain how they support life on earth.
How Living Things are Classified
What does it mean to be alive?
- 1 or more cells (unicellular vs multicelluar)
- reproduce (Asexual vs sexual reproduction)
- pass on traits (DNA, genetics)
- maintain homeostasis
- grow/repair (growth vs development)
- obtain/use energy (Metabolism)
Obtaining Food
spontaneous generation: mistaken idea that living things can arise from nonliving sources.


Viruses & Germs Resources
http://www.seeker.com/search/?q=Viruses+and+germs
Vaccines TImeline
http://www.historyofvaccines.org/timeline
Bacteria

What is the difference between a bacteria & a virus
Bonus Bacteria Video

Cell Theory Ted Talk
http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-wacky-history-of-cell-theory
Cell Structure & Function Online Book
Plant & Animal Cell Info Sheet

Crash Course Animal Cells
In Class Virtual Lab (WKS GIVEN OUT)
What do cells do Simulation
Journey into a cell video
Heterotrophic: Obtain energy from other organism
Autotrophic: Make their own food and create their own energy
spontaneous generation: mistaken idea that living things can arise from nonliving sources.
Biology: The study of life
Where do you find Biology in our world?
preserving the environment
improving the food supply
genetic engineering
human genome
genome: complete genetic material found in an individual
fighting disease
AIDS, HIV, Cancer
Emergence of new disease
gene therapy: replaces defective genes with new genes
cystic fibrosis, hemophilia
Lesson 2 Classifying Life (Book B)
(pages14-21)
3 Domains
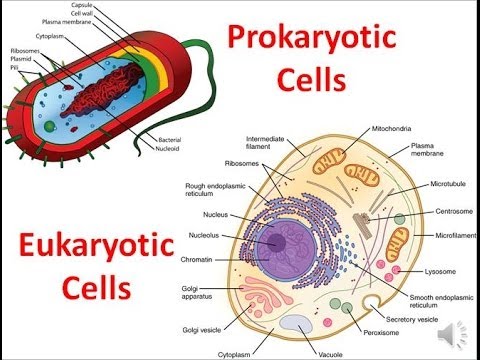
Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic
Water (Cell Book Pg 27, Diversity Book pg 12)
The Importance of Water


Viruses: Diversity of Life Book ( pages 40-45)
(pages14-21)
classification: process of grouping things based on similarities
taxonomy: study of how organisms are classified
binomial nomenclature: two part scientific name.. the genus species name
genus: contain similar organisms
species: similar organisms that can mate and produce offspring that can also reproduce.
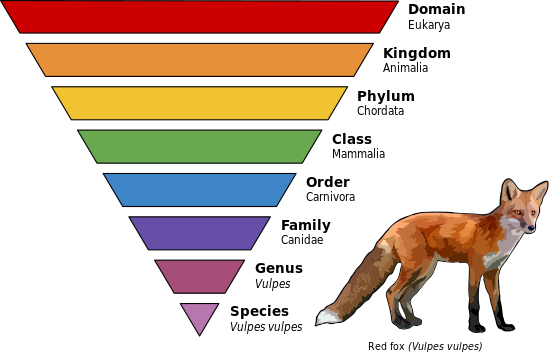
Major Levels of Classification
The taxa in hierarchical order:
- Domain - Archea, Eubacteria, Eukaryote.
- Kingdom - Plantae, Animalia, Fungi, Protists
- Phylum.
- Class.
- Order.
- Family.
- Genus.
- Species - smallest classification.
3 Domains
- Archae
- Bacteria
- Eukarya
Taxonomic Keys are useful tools that help determine the identity of organisms

Hiearchy Structure of a Human
3D Organ Printing Video
Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic
Prokaryotic: Simple, old, primitive, extremophiles, live in harsh conditions, lacks true nucleus (contain domains Archea and Bacteria)
Eukaryotic: more complex, membrane bound organelles, true nucleus, found in Domain Eukarya
Eukaryotic: more complex, membrane bound organelles, true nucleus, found in Domain Eukarya

Water (Cell Book Pg 27, Diversity Book pg 12)
The Importance of Water
- All livign things need water to survive
- Only substance that if found as a solid, liquid and gas
- It is covalently bonded
- They are bonded together by hydrogen bonds
- Has high Cohesion (Attraction between 2 like things)
- Adhesion sticking to other substances
- Does Capillary action (defies gravity, the ability to go up)
- Great SOLVENT (great at dissolving things) Known as the UNIVERSAL SOLVENT
- Hydrophilic vs hydrophobic
- Ability to dissolve more chemicals than any other substance on Earth
- High Heat Capacity: hard to heat up and cool down.. holds temperature well (regulates climate)
- 90% of the liquid in your blood
- Water takes part in most chemical reactions in cells
- Helps cells keep their shape
- Without water life as we know it would would not exist
Viruses: Diversity of Life Book ( pages 40-45)
Is a virus alive?
NO!
- Outside of a cell it does not perform life functions
- Enters cell, takes over life functions, destroys DNA, inserts its own genetic material, takes over ,replicates, kills cell, bursts, spreads virus
What is a virus? A pathogen, which is an agent that causes disease.
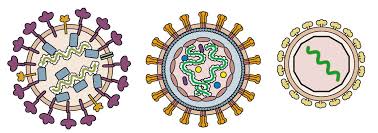
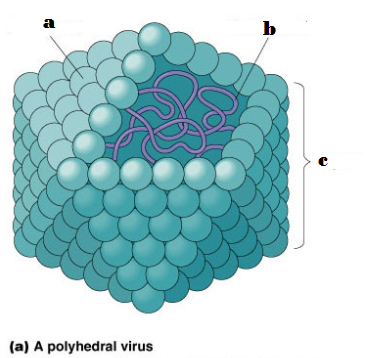
Viral Structure
Can contain RNA or DNA
RNA Virus: HIV, flu, rabies
DNA Virus: warts, chicken pox, mono
Shapes
- enveloped
- helical
- polyhedral
More:
Vocab
bacteriophage: virus that infects bacteria.
Video Bacteriophage
http://www.seeker.com/the-secret-soviet-virus-that-helps-kill-bacteria-2141944345.html
Video Bacteriophage
http://www.seeker.com/the-secret-soviet-virus-that-helps-kill-bacteria-2141944345.html
vaccine: virus stimulating an immune response
Plants and animal can get a virus!
Cells Alive
How Flu Viruses Attack
How Flu Viruses Attack
The first ever vaccine was created when Edward Jenner, an English physician and scientist, successfully injected small amounts of a cowpox virus into a young boy to protect him from the related (and deadly) smallpox virus. But how does this seemingly counterintuitive process work? Kelwalin Dhanasarnsombut details the science behind vaccines.
For 10,000 years, humanity suffered from the scourge of smallpox. The virus killed almost a third of its victims within two weeks and left survivors horribly scarred. But Simona Zompi commends the brave souls – a Buddhist nun, a boy, a cow, a dairymaid and physician Edward Jenner – who first stopped the spread of this disastrous disease, to make us smallpox-free today.
Viruses & Germs Resources
http://www.seeker.com/search/?q=Viruses+and+germs
Vaccines TImeline
http://www.historyofvaccines.org/timeline
How to Become an Epidemiologist?
CareerBuilder Videos from funza Academy.
CareerBuilder Videos from funza Academy.
Bacteria
What is the difference between a bacteria & a virus
Bonus Bacteria Video
Crash Course Bacteria
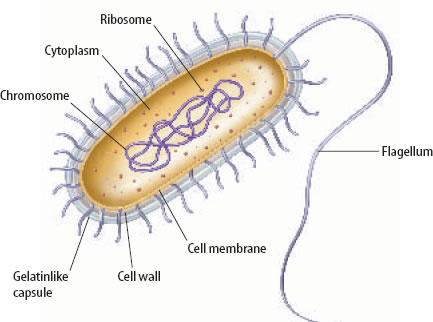
Bacteria: single celled PROKARYOTIC organism. Their genetic material in their cells is NOT in a nucleus.
Bacterial Shapes:
Sphere Shaped
Rod Shaped
Spiral Shaped
Respiration
Cellular respiration: process of breaking down food to create energy
Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction: the process is called BInary Fission
Sexual Reproduction: the process is called conjugation
endospore: inside of a bacteria and contains the genetic material
Role of Bacteria In Our World
- Oxygen Production
- Food Production
- Health and Medicine
- Environmental Clean up
- Environmental Recycling
- decomposers: break down large, complex chemicals in dead organisms into small, simple chemicals.
Gram Stain
Gram negative cell walls contain a thin peptidoglycan layer (without techoic acids) that is surrounded by a thick plasma membrane. Gram positive bacteria will stain purple because of their thick peptidoglycan cell wall.


TedEd: What causes antibiotic resistance?http://ed.ted.com/lessons/how-antibiotics-become-resistant-over-time-kevin-wu
Right now, you are inhabited by trillions of microorganisms. Many of these bacteria are harmless (or even helpful!), but there are a few strains of ‘super bacteria’ that are pretty nasty -- and they’re growing resistant to our antibiotics. Why is this happening? Kevin Wu details the evolution of this problem that presents a big challenge for the future of medicine.
Attack of the Super Bug
Cell Theory Ted Talk
http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-wacky-history-of-cell-theory
Cell Theory
There are 3 Parts
- All living things are made up of 1 or more cells
- Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in all organisms
- All cells arise from existing cells
Cell Theory Song
Cell Structure & Function Online Book
Plant & Animal Cell Info Sheet
Crash Course Animal Cells
Crash Course Plant Cells
In Class Virtual Lab (WKS GIVEN OUT)
What do cells do Simulation
Journey into a cell video
Cell Structure Video

No comments:
Post a Comment